Shielding the Mind with Flow: Attention Allocation and Auditory Event-related Potentials under Varying Mental Workload
Oct 18, 2024· ,,,·
1 min read
,,,·
1 min read
M.Sc. Katharina Lingelbach
Anna Vorreuther
Elias Moll
Mathias Vukelić
 Flow State EEG Analysis
Flow State EEG AnalysisAbstract
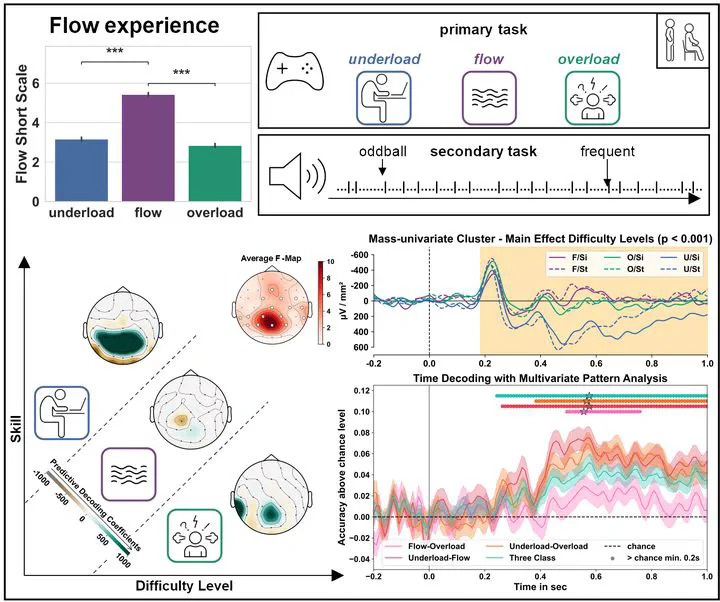
Attention is vital for prioritizing relevant information and shielding against distractions. This study investigates how varying levels of mental workload influence auditory attention, cognitive resource allocation, and the experience of flow using a dual-task paradigm. Through EEG analysis, spatiotemporal clustering, and multivariate pattern decoding, we identify flow as a state that shields attention from distractions, enhancing task engagement and performance.
Type
Publication
European Journal of Neuroscience (Submitted, Under Review)
This study highlights the cognitive and neural mechanisms of the flow state, employing EEG-based measures to distinguish between underload, flow, and overload conditions. Flow, characterized by deep task engagement and positive valence, functions as an attentional shielding mechanism, facilitating task performance while reducing sensitivity to external distractions. The findings are critical for applied neuroergonomics, offering implications for workplace design, educational tools, and mental health strategies.